Entrepreneurial Mindset for Successful Life
Erasmus+ project
“Entrepreneurial Mindset for Successful Life” (EMSL) is a two-year Erasmus + project in which four different European Schools are working together to reduce youth unemployment.
Mobilities
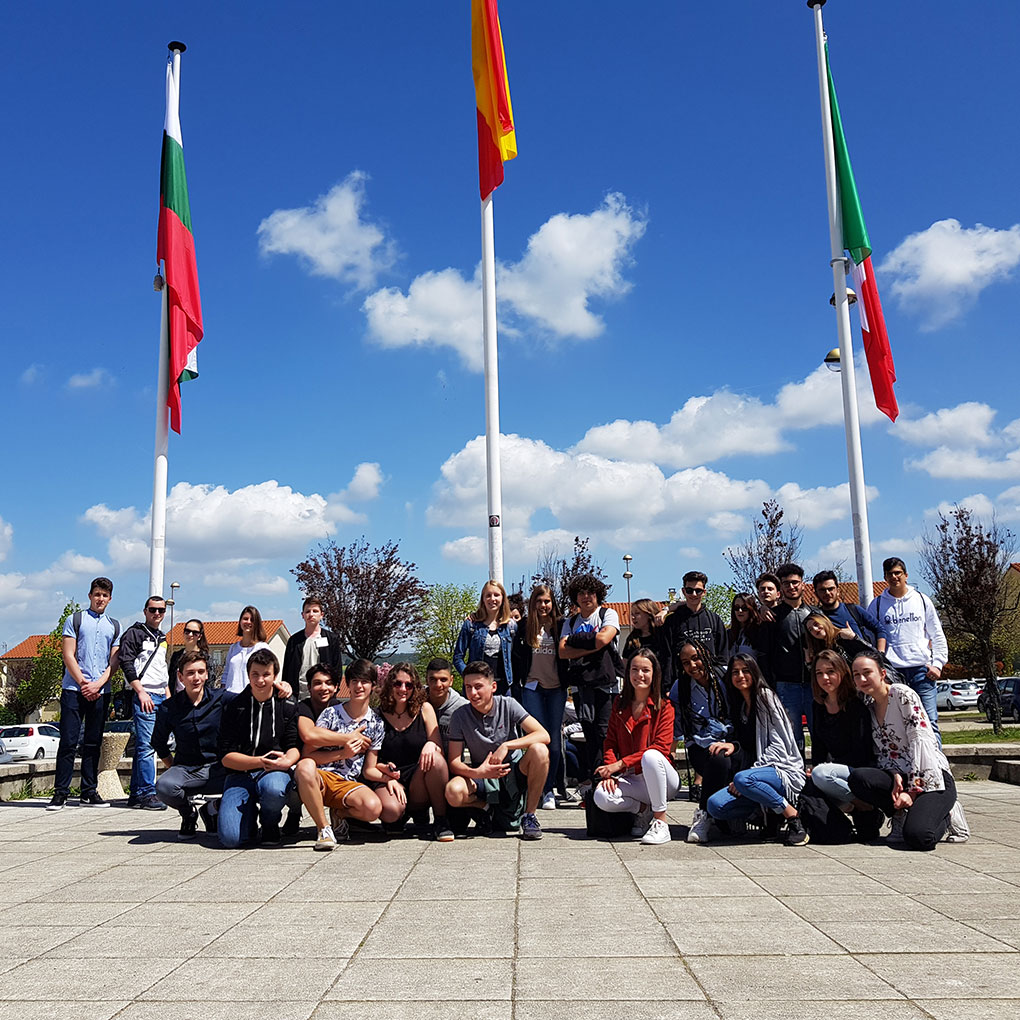
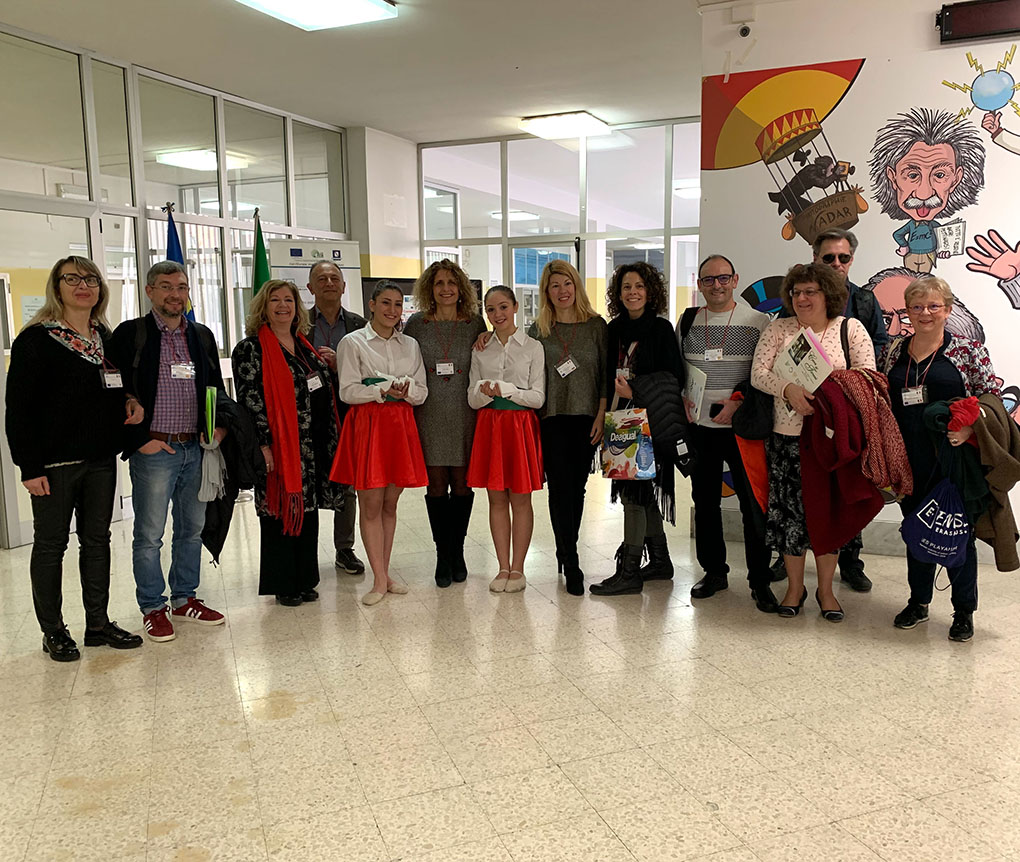
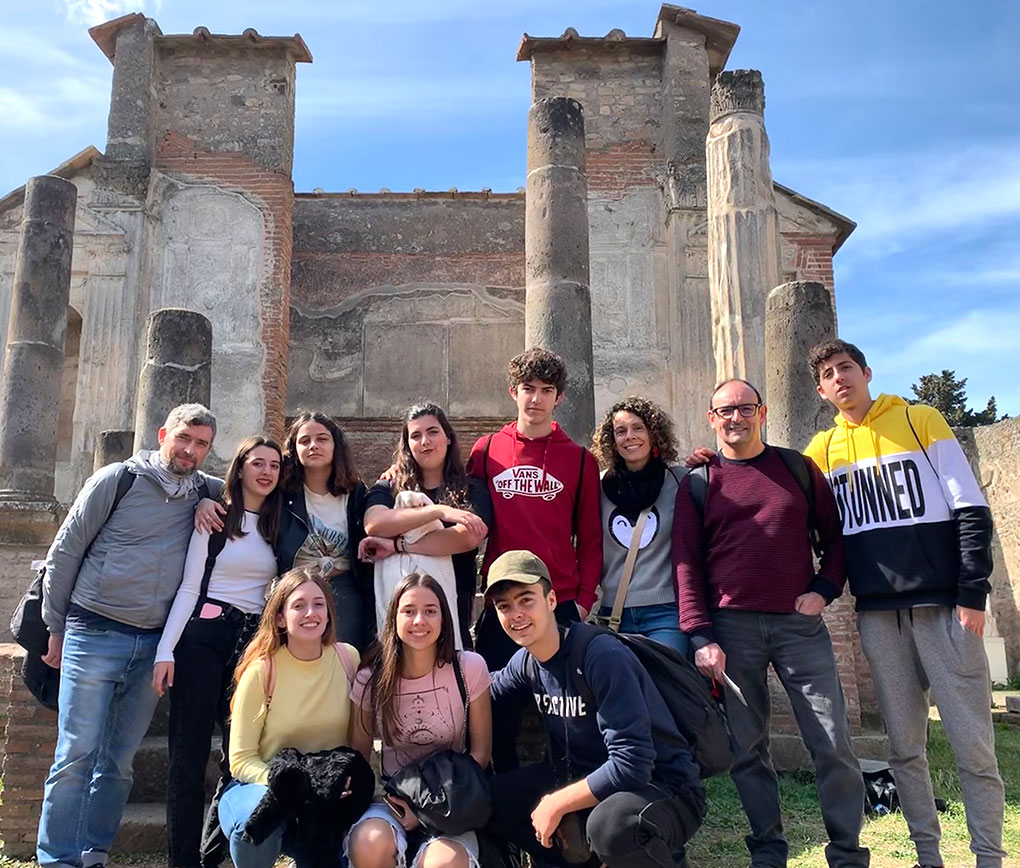
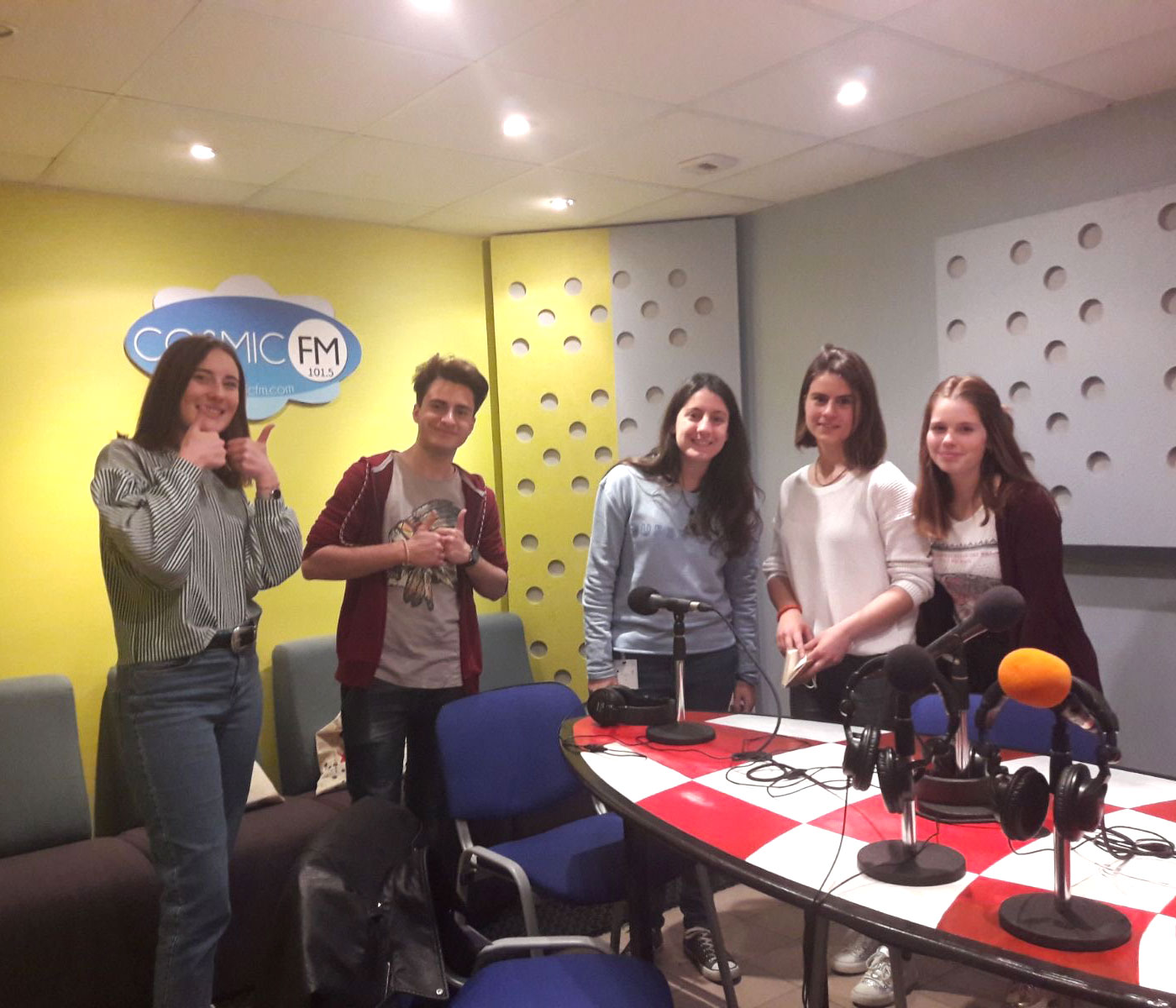
Our international meetings
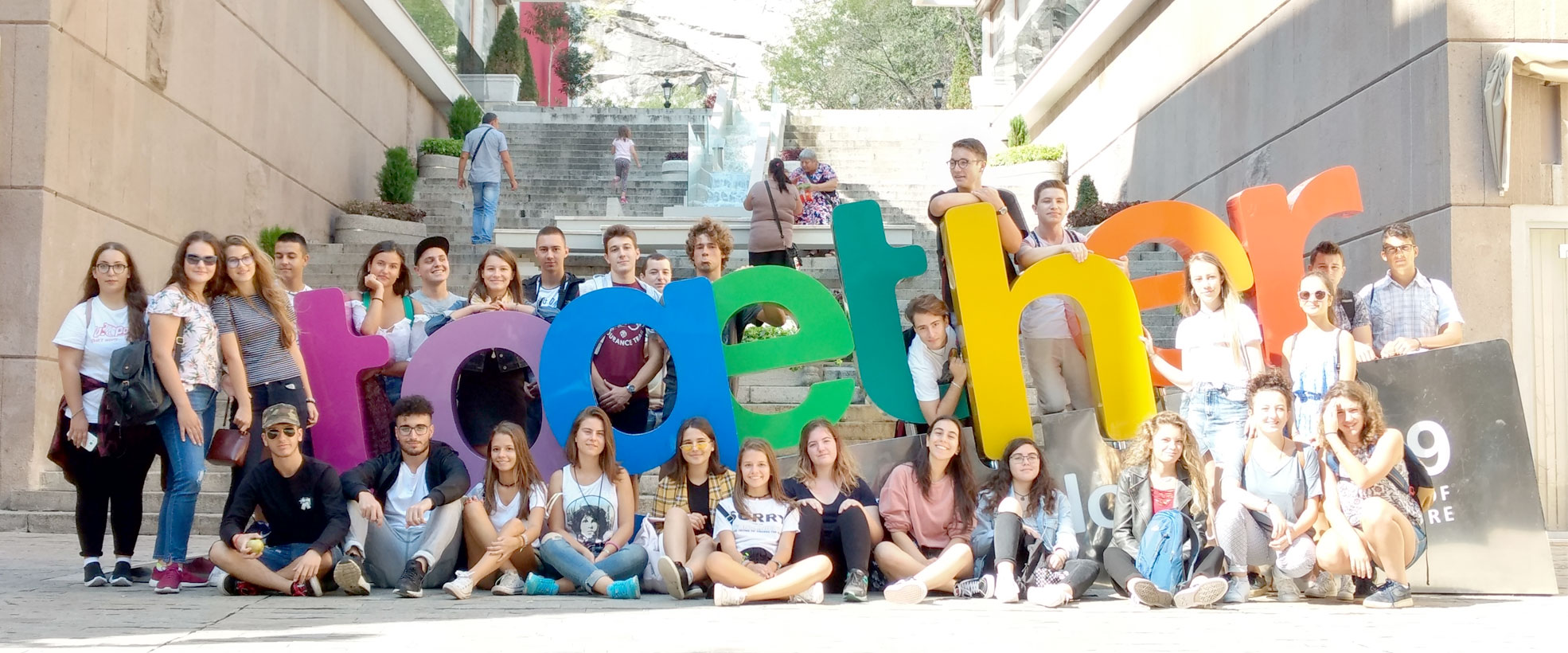
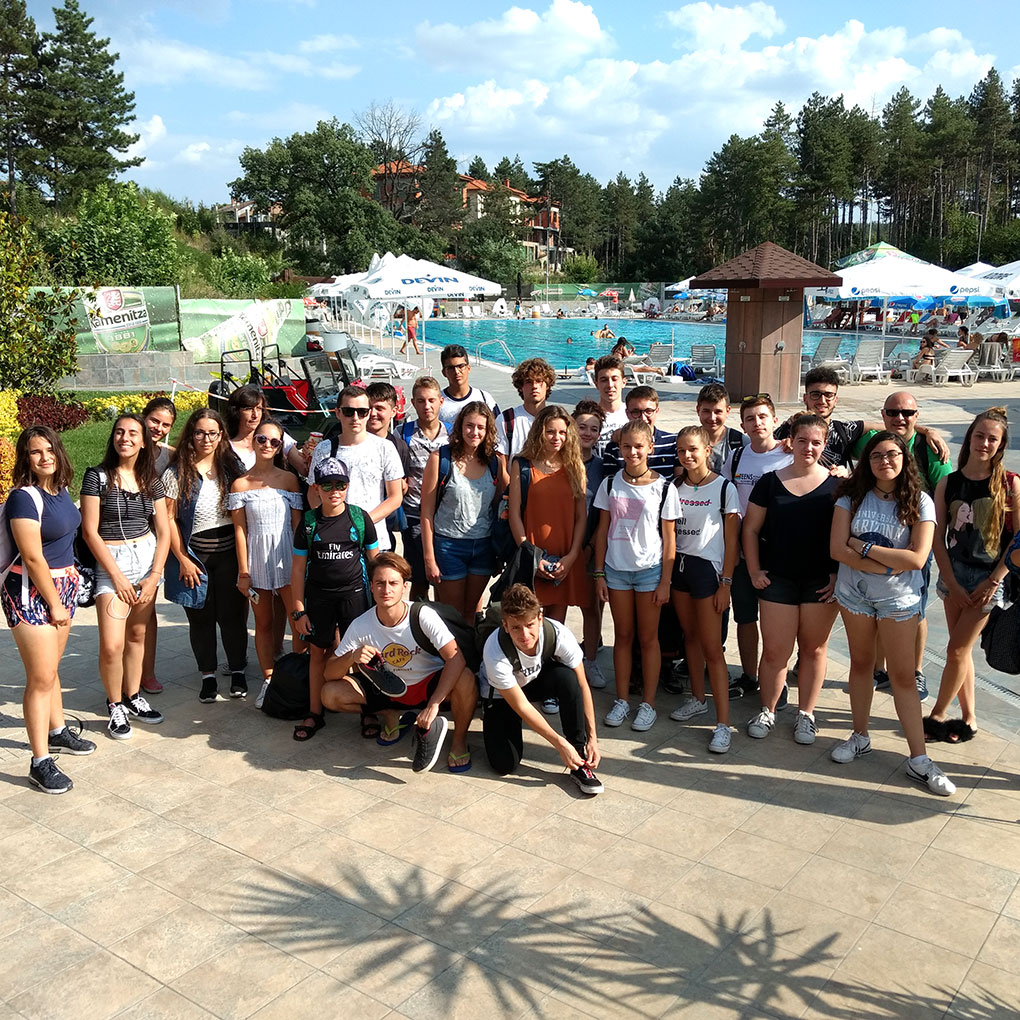
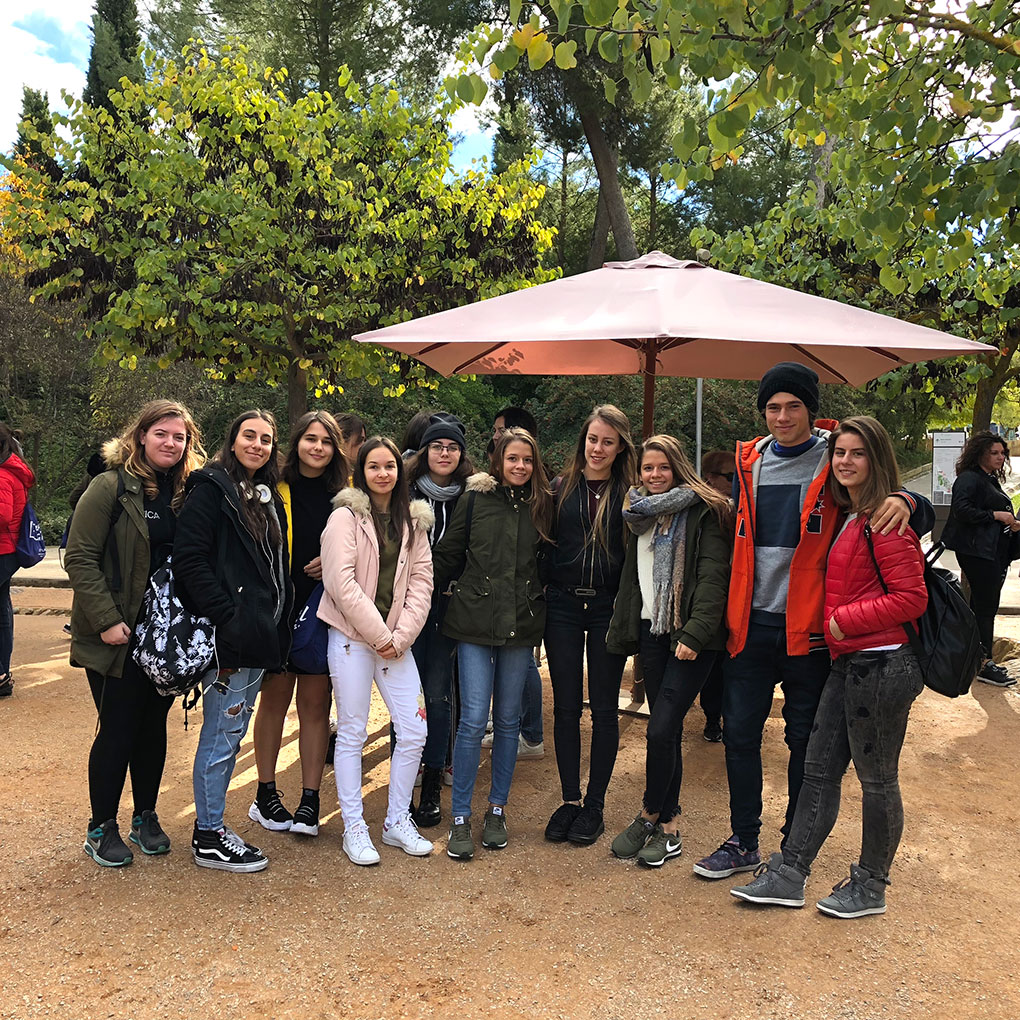
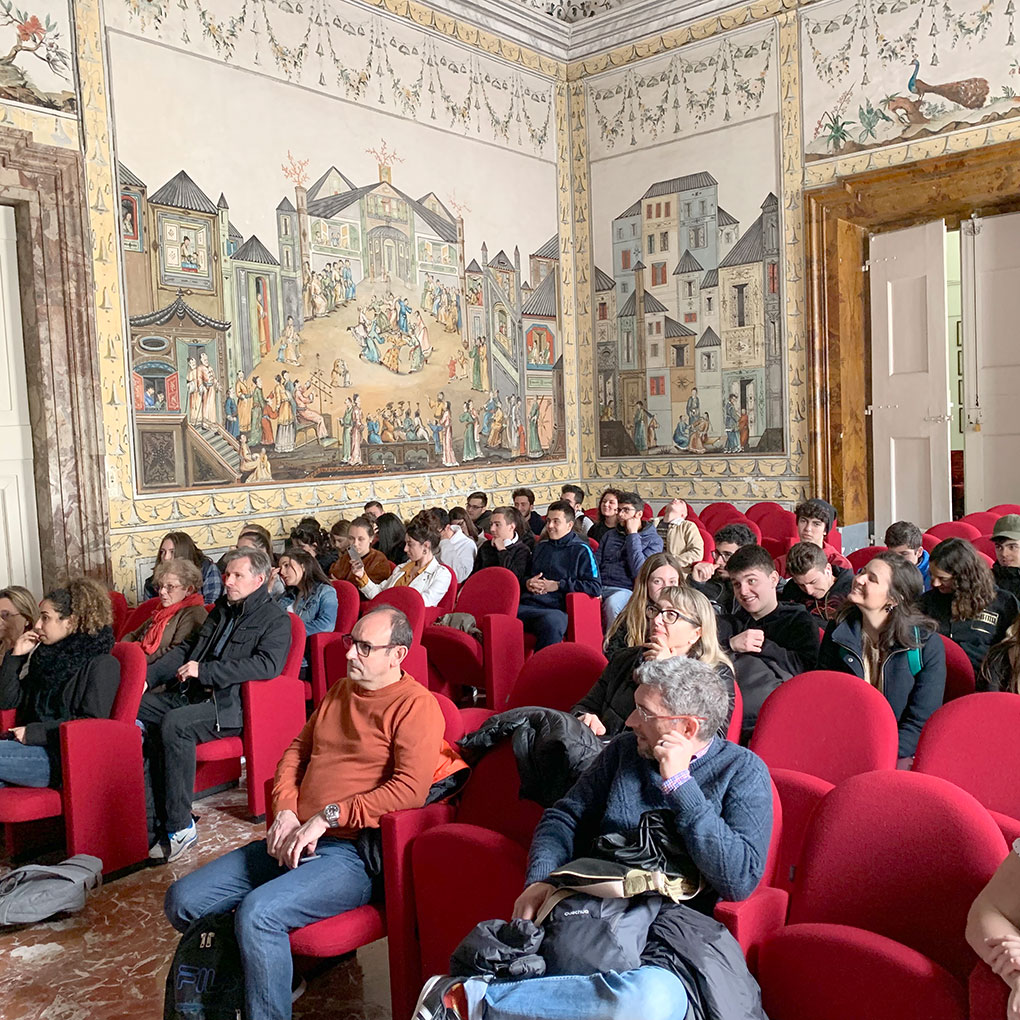
Our international meetings began in Spain in November 2017. In 2018 we visited France, Bulgaria and again Spain. In 2019 we visited Italy and France. You can see photos of all our mobilities.
Evaluation mechanisms for a quality project
Throughout the project, each activity was evaluated by all participants. These allowed us to implement improvement measures in later activities.
After each questionnaire we carry out a SWOT analysis of the results.
Answers of students and teachers after an international meeting at IES Playamar.
Our project in numbers
It was simply amazing. Having the opportunity to work with an international team helped me so much and I genuinely enjoyed every second of the meeting.
This meeting was a wonderful experience that I would repeat if I could. It helps me to improve my english and other languages, to know more about other cultures, to meet friends and to learn information from the workshops that will helps me in my professional future.
I Will never forget this experience.
This experience was extraordinary and really nice. I really want to make it again.
I enjoyed a lot, it was one of the best experiences in my life and I think, no matter how much, that everyone learned something with it.
It was a very good experience for me. It was very interesting to see how other families work in other countries, the different kind of food that people eat, all in all, new cultures and people. I would love to repeat it.